Whether you are a business owner finalizing a client deal, an HR manager onboarding a new employee, or a freelancer securing a project, knowing whether a signature is legally binding is critical.
Legal signatures, whether handwritten, electronic, or digital, serve as proof of intent and agreement. Laws such as the ESIGN Act, UETA, and eIDAS define what constitutes a contract signing. Understanding these requirements ensures compliance, protects your rights, and prevents contract disputes.
What is a legal signature?
A legal signature is any mark, symbol, or process that demonstrates a person’s intent to agree to the terms of a document, making it legally enforceable. This includes handwritten names, initials, scribbles, typed names, electronic signatures, and digital signatures.
For example:
- A startup founder signing a client NDA to protect confidential information.
- An HR manager is completing an employment contract for a new hire.
- A freelancer signing a project agreement or proposal digitally.
- A business owner is finalizing a vendor or supplier contract.
Laws such as the ESIGN Act (U.S.) and eIDAS (EU) recognize electronic and digital signatures as legally binding if they meet requirements like intent, authentication, attribution, and record retention.
Ensuring signatures meet these legal standards protects individuals and organizations from disputes, enforces contractual obligations, and guarantees that agreements—whether domestic or international—hold up in court.
Streamline your signature workflow today
HyperStart helps you create legally enforceable signatures quickly and securely. Save time, reduce errors, and keep all your contracts organized in one platform.
Book a DemoWho needs legal signatures?
Legal signatures are crucial for anyone involved in agreements, contracts, or official documents where enforceability is a key consideration. Different professionals rely on them in specific ways:
- Business Owners & Startups: Use legal signatures to finalize client contracts, partnership agreements, and vendor or supplier contracts. For example, a startup founder signing an NDA with a new client ensures confidential information remains protected.
- HR Professionals & Recruiters: Secure employment contracts, offer letters, and onboarding documents. A legally binding signature ensures that employees understand and agree to the company’s policies, benefits, and responsibilities.
- Freelancers & Consultants: Formalize project agreements, proposals, and invoices. Signing electronically ensures clients acknowledge the scope, deliverables, and payment terms, minimizing disputes.
- Legal Professionals: Verify and enforce contracts, settlements, and other legal documents. Legal signatures provide proof of intent and compliance, essential in litigation or arbitration.
- Enterprises & Remote Teams: Manage vendor agreements, cross-border contracts, and team approvals efficiently. Electronic and digital signatures allow large teams to execute documents securely from anywhere, while maintaining legal enforceability.
Understanding who needs legal signatures and for what types of documents ensures that agreements are enforceable, disputes are minimized, and all parties’ rights are protected.
Electronic signatures have the same legal validity as handwritten signatures under laws like the Uniform Electronic Transactions Act (UETA). They must show clear intent to sign, consent to conduct business electronically, be associated with the signed record, and have proper record retention.
Electronic signatures cannot be denied legal effect solely because they are in electronic form, and parties must agree to transact electronically. Security measures such as verification processes help ensure authenticity and enforceability.
What are the requirements for a legally binding signature?
Not every signature automatically makes a document legally enforceable. To ensure a signature is recognized by law, it must meet specific requirements that prove the signer’s intent, consent, and the authenticity of the document. These rules apply to both handwritten and electronic signatures.
Intent to sign
The signer must clearly indicate their intention to agree to the terms. For instance, a client clicking “I agree” on an online contract or an employee signing an offer letter demonstrates clear intent. Without this, the signature may be considered invalid.
Consent and understanding
The signer must voluntarily accept the terms. This is why employees should review onboarding documents, freelancers should read contracts before signing, and business partners should have access to agreements before execution.
Signature attribution
The signature must be traceable to the individual. For electronic signatures, this includes an audit trail showing the signer’s name, email address, IP address, and timestamp. This ensures accountability and prevents disputes over authenticity.
Record retention
Legally binding documents must be easy to retrieve for reference or legal purposes. For example, HR teams keep employment contracts for compliance audits, while businesses maintain vendor contracts for potential disputes.
Security and protection
The signature must be tamper-proof from unauthorized changes. Digital signatures with encryption, verification codes, or certificate-based authentication provide added protection, especially for sensitive agreements.
Meeting these requirements ensures that agreements—from NDAs and employment contracts to vendor deals and freelance agreements—are enforceable in court. It protects all parties involved, prevents disputes, and ensures compliance with laws such as the ESIGN Act (U.S.) and eIDAS (EU).
Electronic signatures are legally valid when the signer intends to authenticate the document and the signature is securely linked to the record. Compliance with laws like the ESIGN Act (U.S.) and eIDAS (EU) ensures enforceability, provided there is consent, authentication, and audit trails. These measures reduce disputes and facilitate faster, cost-effective transactions globally.
Read
What are the different types of legal signatures?
Legal signatures come in several forms, each suitable for different documents and purposes.
1. Physical or wet signatures
Physical or wet signatures are handwritten signatures made in person. They are commonly used for high-value agreements, government documents, or notarized contracts. For example, signing a property sale or a mortgage agreement usually requires a wet signature along with witness verification.
2. Electronic signatures (eSignatures)
Electronic signatures (eSignatures) are created digitally, such as typing a name, drawing it on a touchscreen, or uploading an image of a handwritten signature. Laws such as the ESIGN Act, eIDAS, and India’s IT Act recognize e-signatures as legally binding when intent, consent, and record retention are ensured. Businesses, HR teams, and freelancers often use eSignatures to quickly sign contracts, NDAs, or proposals while maintaining their enforceability.
3. Digital signatures
Digital signatures are a type of electronic signature that adds encryption and authentication, ensuring the authenticity of the signature and the integrity of the document. They are often used in vendor agreements, financial approvals, and software licensing contracts where tamper-proof security is essential. While all electronic signatures are digital signatures, digital signatures offer stronger security through encryption and authentication, making them ideal for high-risk or sensitive contracts.
4. Faxed or scanned signatures
Faxed or scanned signatures involve sending an electronic image of a handwritten signature. While legally acceptable in many situations, they are less secure than digital signatures and are usually used when other signing tools are unavailable.
Understanding these types helps organizations, freelancers, and professionals select the right method for each document, ensuring enforceability, security, and contract compliance.
What are the use cases of legal signatures?
Legal signatures are essential across various roles and industries, ensuring agreements are enforceable, protecting rights, and streamlining operations. The following table highlights key use cases and their practical benefits:
| Audience / Role | Use Case | Example | Benefit / Context |
| Business owners & startups | Client contracts, vendor agreements, partnership deals | A startup founder signing a non-disclosure agreement (NDA) with a new client | Protects sensitive business information, ensures enforceability of agreements, and minimizes the risk of disputes with partners or clients. They make business operations more secure and trustworthy. |
| HR professionals & recruiters | Employment contracts, offer letters, and onboarding documents | HR manager securing an employment agreement for a new hire | Confirms that employees understand company policies, benefits, and responsibilities. They help HR prevent misunderstandings, non-compliance, or legal challenges related to employment terms. |
| Freelancers & consultants | Project agreements, proposals, and invoices | Freelancer signing a project proposal digitally | Provides a legally enforceable record that clearly defines project scope, deliverables, and payment terms. Protects freelancers from non-payment or disputes and ensures clarity with clients. |
| Legal professionals | Contracts, settlements, legal documents | Lawyer verifying a settlement agreement | Serves as proof of intent and compliance, which is essential in court, arbitration, or legal audits. They help maintain the integrity of agreements and evidence. |
| Enterprises & remote teams | Vendor agreements, cross-border contracts, and team approvals | Remote teams signing contracts digitally across multiple locations | Enables multiple parties to sign securely from anywhere while ensuring the agreement is legally binding. Streamlines workflows, reduces delays, and maintains compliance across borders. |
Never worry about compliance again
HyperStart ensures every signature meets legal requirements and is fully auditable. Stay compliant while giving your team and clients a signing experience.
Book a DemoWhat are the benefits of legally binding signatures?
Legally binding signatures do more than formalize agreements—they protect parties, streamline operations, and provide legal certainty for businesses, HR teams, freelancers, and legal professionals. Here’s why they matter:
1. Ensure enforceability in court
A legally binding signature provides clear evidence that all parties agreed to the terms of a contract. This applies to NDAs, client contracts, partnership agreements, and vendor deals. Having proper signatures ensures that if a dispute arises, the agreement can be presented as valid proof in court, safeguarding your business or freelance interests.
2. Reduce disputes and legal risks
By creating a documented record of consent, misunderstandings and conflicts are minimized. This is particularly important for HR agreements, employment contracts, and project scopes. Tools like Hyperstart enhance this by providing audit trails, timestamped records, and compliance features, giving both parties confidence that the document cannot be tampered with.
3. Streamline operational efficiency and workflow
Digitally signing agreements speeds up approvals and reduces administrative bottlenecks. Whether onboarding a new employee, approving vendor contracts, or finalizing client agreements, teams no longer need to wait for in-person signatures, allowing business processes to move faster and teams to focus on productive work.
4. Save costs and time
Traditional paper-based workflows require printing, mailing, and storing documents, which can be expensive and time-consuming. Legal electronic signatures eliminate these steps, reducing operational costs while accelerating project timelines. This is especially useful for businesses handling large volumes of contracts or freelancers managing multiple client agreements.
5. Increase accessibility
Electronic and digital signatures allow documents to be signed from anywhere, at any time, and on any device. This makes collaboration easier for remote teams, international clients, and freelancers. Legal validity is maintained while providing the convenience of signing on the go.
How to make signatures legally binding using HyperStart
Ensuring that a signature is legally valid requires following clear steps. While traditional methods focus on physical signatures, modern platforms like HyperStart make it easy to execute legally binding contracts digitally. Here’s a detailed guide:
1: Review the document thoroughly
Before signing, carefully read every clause, term, and condition. Ensure you understand your obligations, rights, deadlines, and penalties. For example, employment agreements, client contracts, and vendor deals often contain clauses that can affect payments, confidentiality, and responsibilities. Reviewing the document ensures informed consent and reduces the risk of disputes.
2: Prepare the contract in HyperStart
Once all internal approvals are complete in HyperStart, the workflow will show the contract as Ready for Signature. At this stage, you can:
- Add stamp paper if required.
- Upload a pre-signed PDF if the document was signed externally.
- Proceed to send it for signature using HyperStart’s integrated eSignature options.
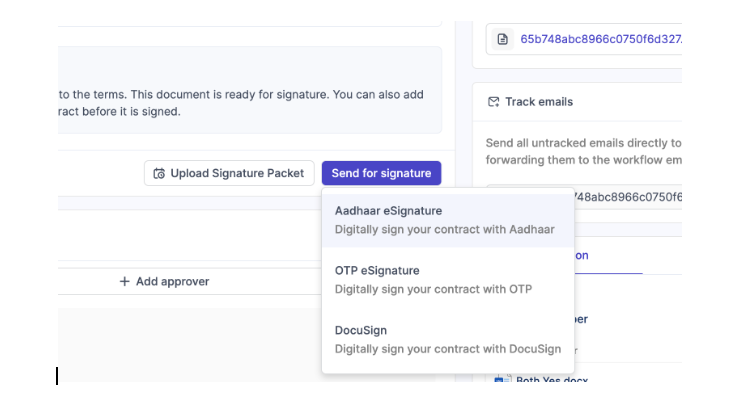
3: Select the type of signature
HyperStart supports multiple signature providers:
- DocuSign or Adobe eSignature – redirects you to DocuSign for the signing process.
- OTP-based eSignature – uses mobile/email verification to confirm signer identity.
- Aadhaar eSignature – a secure Aadhaar-based signing option.
4: Add participants and assign roles
- Enter the name and email of each signer.
- For multiple signers, click Add signer to create individual signer cards.
- You can also add recipients who should receive a copy of the signed contract for review or record-keeping. HyperStart even suggests recipients based on activity logs, ensuring key stakeholders stay informed.
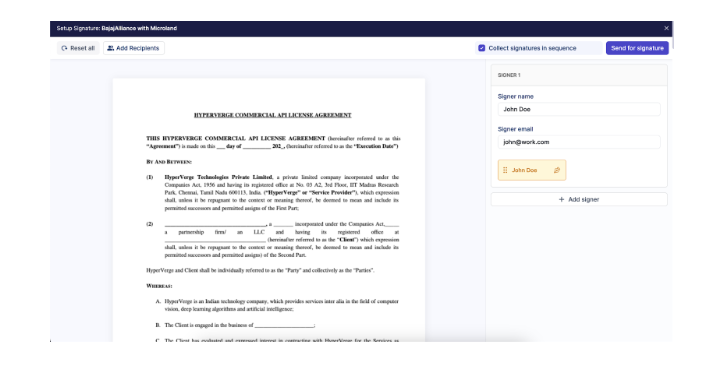
5: Place signature fields on the document
- Drag and drop signature fields onto the document at the locations where each signer needs to sign.
- Fields can be resized, and multiple instances can be assigned to the same signer if necessary.
- This ensures that each signature is clearly linked to the correct party, maintaining enforceability and traceability.
6: Decide the signing sequence
- Choose Collect signatures in sequence if signatures must follow a specific order. This is best for hierarchical approvals or sequential client-vendor agreements.
- Leave unchecked for parallel signing, where all signers receive requests simultaneously, speeding up the process for documents requiring multiple approvals at once.
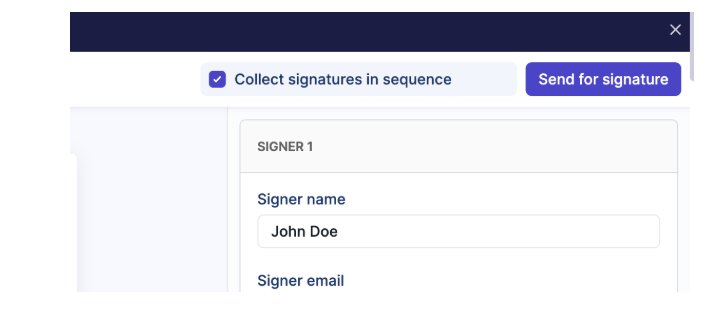
7: Verify settings and send for signature
- Review all participant details, signature placements, and sequence settings.
- Click Send for signature.
- Signers will receive an email with instructions to complete the signing process.
8: Track and finalize the signed contract
- HyperStart maintains an activity log, allowing you to monitor which participants have signed and who is pending.
- Once all signatures are collected, the contract is legally binding and securely stored in HyperStart.
- Any recipients you added receive a copy of the finalized contract, ensuring transparency and proper record-keeping.
9: Maintain records for legal compliance
- Legally binding contracts must be retrievable for audits, disputes, or compliance purposes.
- HyperStart automatically keeps signed contracts securely stored, maintaining encryption and audit trails for maximum legal protection.
Make every signature legally enforceable with HyperStart
Legally binding signatures are crucial for ensuring contracts, agreements, and important documents are enforceable, reducing disputes, and protecting your business from personal interests. HyperStart – contract management software makes this process simple, secure, and fully compliant.
By leveraging trusted eSignature options like DocuSign, Adobe, and OTP-based eSignatures, HyperStart, which provides a contract signing solution, ensures that every signature meets legal standards for intent, verification, and record retention. Its workflow features—such as drag-and-drop signature fields, sequential or parallel signing, and recipient tracking—make signing contracts faster, more efficient, and transparent.
Whether you’re onboarding employees, formalizing client agreements, or managing vendor contracts, HyperStart empowers you to create legally enforceable signatures with confidence. With secure storage and audit trails, every signed document is fully compliant and protected, giving you peace of mind.
HyperStart ensures that every signature you collect is not only easy to obtain but also legally valid, helping you streamline operations while staying compliant.












