Signing a contract takes seconds. But if you’re scaling a SaaS startup, running a legal firm, managing financial contracts, or navigating logistics operations, knowing when to use an electronic signature vs a digital signature can directly affect your compliance risk, deal speed, and legal protection.
According to Adobe’s Total Economic Impact Report, replacing manual signature collection saves ~1.5 hours per transaction, accelerating deal cycles across departments. What’s more, companies that adopt digital signature platforms can free up 3 full-time compliance employees for higher-impact work by automating repetitive tasks.
Furthermore, regulatory bodies, courts, and businesses are increasingly recognizing that not all electronic signatures carry equal legal weight or security assurances.
For legal, compliance, and risk teams, understanding the difference can determine:
- Whether your signed agreements hold up in court
- If you’re compliant with international regulations
- How vulnerable are your documents to tampering or fraud
In this guide, we’ll break down the core differences, cut through the jargon, and help you choose the right solution for your business, whether you’re handling simple NDAs or high-stakes financial transactions.
What is an electronic signature?
An electronic signature (e-signature) is a digital method of demonstrating agreement to the terms and conditions of a document or contract. It is the digitized equivalent of a handwritten wet signature, legally binding the signer to the document’s content. E-signatures can take multiple forms:
- Typing your name into an electronic form
- Clicking an “I accept” button
- Inserting a scanned image of your handwritten signature
- Using a touchscreen to draw your name on a tablet
The core idea is to sign, even if the legal signature isn’t backed by sophisticated digital signature technology. That makes both electronic signatures and digital signatures legally binding under many laws, provided certain conditions are met.
Global legal validity of electronic signatures
In most countries, electronic signatures carry legal validity if they meet basic standards of consent, attribution, and intent:
- United States: ESIGN Act (2000) and UETA (1999) grant e-signatures the same weight as pen-and-paper.
- European Union (EU): Under the eIDAS Regulation, different levels of e-signatures offer varying legal strength.
- India: The Information Technology Act (ITA-2000) validates e-signatures, including Aadhaar-based identity verification.
Types of electronic signatures
Here’s a breakdown to help you choose the right type of electronic signature based on your document needs.
| Type | What It Is | Which Signature to Use When? |
| Simple Electronic Signature (SES) | The most basic form—checking a box, typing a name, clicking “I accept” | For low-complexity documents: internal HR forms, employee policy acknowledgments, order forms |
| Advanced Electronic Signature (AES) | Adds some security: links the signature to the signer’s identity and detects tampering | For medium-complexity documents: sales contracts, standard vendor agreements, employment contracts |
| Qualified Electronic Signature (QES) | Highest assurance—identity fully verified by a trusted third party, with strong cryptographic protection | For high-complexity or regulated documents: financial transactions, cross-border legal contracts, healthcare records, government filings |
To sum up, businesses handling sensitive digital documents often require stronger identity assurance, secure audit trails, and cryptographic protection areas where digital signature technology excels.
How to create electronic signatures: Step-by-step process
Here’s where it gets practical. Creating an electronic contract signature is refreshingly simple:
- Upload or draw: Scan your handwritten signature, draw it with your finger, or use a stylus
- Type it out: Simply type your name in a signature field
- Click to agree: Check a box or click an “I accept” button
- Authentication layer: Provide an email, phone PIN, or login credentials
The entire process takes seconds, which is why electronic signatures are ideal for contract management workflows where speed is more important than maximum security.
What is a digital signature?
A digital signature is a specific type of electronic signature that uses advanced digital contract management technology to secure an electronic document. Unlike simple e-signatures, a digital signature applies complex cryptographic techniques to ensure:
- Authenticity: Confirms the signer’s identity
- Integrity: Proves the specific document has not been altered
- Non-repudiation: Prevents the signer from denying their action
Digital signature is Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) — a framework of linked encryption keys, digital certificates, and trust service providers (TSPs) that power modern identity assurance systems.
“A cryptographic transformation of data that provides origin authentication, data integrity, and signatory non-repudiation.”
How a digital signature works (simplified flow)
- The digital agreement (document) is run through a secure hash function (e.g., SHA-256), producing a unique “fingerprint”
- This fingerprint is encrypted using the signer’s private key, creating the actual digital signature
- The recipient uses the signer’s public key infrastructure (PKI) to decrypt the fingerprint and compare it to a freshly generated hash of the received document
- If both hashes match, the signed document is confirmed authentic and tamper-free
The role of digital certificates
- Identity verification – You prove you’re you (sometimes with in-person checks).
- Certificate issuance – You’re issued a unique certificate tied to your verified identity.
- Key pair generation – One private key (kept secret), one public key (shared openly).
- Signing – You use your private key to sign.
To generate a digital signature, you need a digital certificate, a kind of virtual passport issued by a Certificate Authority (CA) like Entrust, DigiCert, or an EU Qualified Trust Service Provider (QTSP).
Here’s how the process goes down:
A document that cryptographically links back to you and automatically flags alterations.
Why digital signatures provide strong legal validity
- Cryptographic protection against forgery or tampering makes them a critical part of contract compliance strategies.
- Immutable audit trails for regulators or courts
- Verified signer identity via certified trust service providers
- Full legal validity under qualified electronic signature standards (especially in the EU)
Unlike simple e-signatures, digital signatures include:
When properly implemented, digital signature technology provides a digital equivalent of a paper-based transaction.
Leaving money on the table?
Automate approval cycles with audit trail and version clarity from start to finish. Close deals faster.
Book a DemoDigital signatures vs electronic signatures: Key differences explained
The distinction between electronic and digital signatures has real-world implications for how your signatures are perceived legally, their level of security, and when to use each.
Let’s break down the key differences:
| Feature | Electronic Signature | Digital Signature |
| Definition | Any electronic sound, symbol, or process attached to an electronic document indicating intent to sign | Cryptographic algorithm applied to create tamper-proof digital documents |
| Technology | May involve simple click-wrap agreements or basic form fields | Built on digital signature technology using public key infrastructure (PKI) |
| Identity Assurance | Limited, often based on email verification or IP logs | High, validated through digital certificates issued by accredited trust service providers |
| Private Key Usage | Not applicable | Required — signer uses a private key to generate a signature |
| Tamper Detection | Minimal; documents can be modified after signing | Strong; any changes invalidate the signed document immediately |
| Audit Trail | Basic or none | Comprehensive, immutable audit logs integrated |
| Legal Validity | Accepted in most countries for low-risk transactions | Recognized globally as a paper equivalent for high-risk agreements |
| Regulatory Frameworks | Covered under UETA (US), ESIGN (US), ITA-2000 (India) | Compliant with qualified electronic signature (QES) standards under eIDAS (European Union) |
| Risk Level | Suitable for routine or low-value agreements | Required for high-value, regulated, or sensitive transactions |
The ROI of electronic and digital signature solutions: Cost-benefit analysis
The real value lies in measurable time savings, operational efficiencies, and hard cost reductions businesses achieve when moving from manual, paper-based processes to secure contract automation and digital agreements.
| Category | Traditional Paper Process | Electronic/Digital Process |
| Printing & Paper | ~$6–$20 per specific document | Eliminated |
| Courier/Shipping | ~$10–$50 per contract | Eliminated |
| Physical Storage | Costly filing systems | Fully digital, searchable electronic document repository |
| Admin Processing Time | 1–3 hours per contract | Reduced to minutes |
Best practices for selecting your signature solution
Here’s a structured approach to selecting the right solution for your organization’s digital agreements:
1. Assess document sensitivity and risk profile
- Are you signing low-risk electronic documents, such as internal HR forms or routine vendor approvals?
- Or are you managing digital agreements involving sensitive financial data, healthcare records, government filings, or cross-border transactions?
High-risk, regulated specific documents generally require digital signature technology with strong identity assurance.
2. Evaluate identity verification strength
- Does the solution verify the signer’s identity using secure digital certificates?
- Are private keys securely managed?
- Is there a reliable, court-admissible audit trail?
True digital signature technology offers robust cryptographic authentication.
3. Ensure vendor transparency and scalability
When evaluating signature vendors, ask:
- Are there hidden pricing tiers that limit features?
- Do they lock critical features (like API access or storage) behind premium subscriptions?
- Can the solution scale as contract volume grows?
- Does it integrate with your existing CLM, ERP, or CRM platforms?
Some vendors use complex credit systems or charge extra for features like bulk signing, mobile access, or advanced audit logs — verify total cost of ownership.
4. Prioritize user experience and accessibility
- Is the platform easy for signers to use across different devices?
- Does it support accessibility standards (screen readers, WCAG compliance)?
- Can electronic forms be filled out quickly on a mobile or tablet?
A secure but difficult-to-use system discourages adoption.
5. Consider end-to-end integration with contract management software
- Signature workflows adapt to each specific document’s risk profile.
- Approvals, digital certificates, negotiation history, and audit logs are fully integrated.
- Seamless integrations eliminate data silos, reduce admin work, and streamline contract governance.
Rather than managing separate tools for contract drafting, negotiation, approvals, and signing, HyperStart offers a unified CLM platform where:
With built-in support for Docusign eSignature, Aadhaar eSignature, and OTP-based eSignature, HyperStart allows businesses to apply the right signature strength to every contract signing workflow.
How to use HyperStart for eSignature (Step-by-Step)
HyperStart’s contract signing software streamlines the contract signing process by integrating with trusted eSignature solutions, so you can move fast without leaving the platform. Here’s how to go from approved contract to signed agreement in a few simple steps.
Step 1: Add a Stamp or Start Signature Setup
- Click Add stamp if you need one.
- Otherwise, click Send for signature to proceed.
Step 2: Choose Your Signature Method
- Select your preferred signature type: DocuSign, Aadhaar eSign, or OTP-based eSign
Step 3: Add Signers
- Click Add signer to input the name and email for each participant.
- Add as many signers as needed—each will have their signature field card.
Step 4: Place Signature Fields
- Drag and drop signature blocks onto the contract.
- Resize as necessary.
- You can add multiple signature fields per signer.
Step 5: Choose Signature Order
- Sequential: Signers sign one after another in your specified order.
- Parallel: All signers receive the request at the same time.
- You can drag and rearrange signer cards to change the sequence.
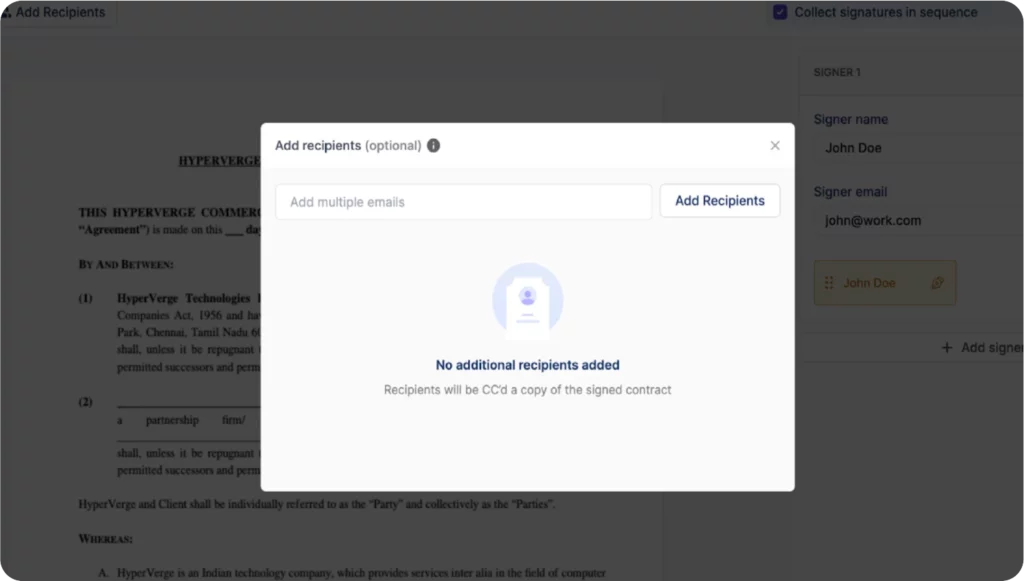
Step 6: Add Contract Recipients (Optional)
- Click Add recipients (top left of composer).
- Enter the email addresses of people who should receive a copy of the signed contract.
- HyperStart also suggests relevant recipients from your activity log.
Step 7: Final Check and Send
- Review all signer and recipient details.
- Click Send for signature (top-right) to initiate the process.
Made a mistake? Use the Reset all button to wipe the composer and start fresh.
HyperStart in Action
Learn how one consumer goods startup slashed signature delays by 90%
When a fast-growing consumer goods startup came to HyperStart, their contract process was complicated. Manual stamp handling, scattered tools, and endless back-and-forth just to get a vendor contract signed.
With HyperStart’s built-in eSignature options (Docusign, Aadhaar eSign, and OTP-based flows), they streamlined everything. What used to take 4–5 days now gets signed in under 24 hours.












